Textile engineering is a branch of engineering that deals with the science and technology of
manufacturing textiles, including fibers, yarns, fabrics, and clothing. It involves the design, development,
and production of various textile materials, as well as the study of their properties and applications.
Textile engineers are responsible for developing new materials and processes that improve the quality,
durability, and functionality of textiles, while also considering the environmental impact of textile
production.

Work description
The work of a textile engineer involves designing, developing, and testing new textiles and textile
products. They work on the development of new fabrics, fibers, and yarns, as well as the improvement
of existing materials.
Textile engineers also work on developing new processes for the production of textiles, such as
weaving, knitting, and dyeing. They are responsible for ensuring that the textiles they develop meet
specific requirements in terms of strength, durability, color fastness, and other properties.
In addition to developing new textiles, textile engineers also work on improving the efficiency of textile
manufacturing processes. They may work on designing new machinery or modifying existing equipment
to increase production rates and reduce costs. Textile engineers also collaborate with other
professionals, such as fashion designers and materials scientists, to develop new products and
applications for textiles.
As part of their work, textile engineers may also need to conduct research and testing to determine the
properties of different materials and the effects of various manufacturing processes on those materials.
They may use specialized equipment and software to analyze data and create models to predict the
performance of different textiles.
High Demand
Textile engineering offers a wide range of job opportunities in various industries, such as
fashion, sportswear, home textiles, and automotive textiles.
Lucrative salaries
It is a growing field with a high demand for skilled professionals, especially in developing
countries with a growing textile industry.
Opportunities for innovation
Textile engineers work on developing new materials and processes, which can be both
challenging and rewarding.
Versatility
The industry is constantly evolving, providing opportunities for ongoing learning and
professional development.
Flexibility
Textile engineering has a positive impact on society by contributing to the development of
sustainable and environmentally friendly materials and production processes.
Job satisfaction
The work of textile engineers is often collaborative, allowing for the development of strong
teamwork and communication skills.
High stress
The textile industry can be highly competitive, with many skilled professionals competing for
limited job opportunities.
Long hours
The work can be physically demanding, especially in roles that involve working with machinery
or in production environments.
Competitive field
The industry can be heavily influenced by economic fluctuations and may be vulnerable to
changes in consumer demand.
Constant learning
Textile engineering can involve working long hours, including evenings and weekends, to meet
production deadlines.
Isolation
The work may require extensive travel, including overseas, which can be challenging for those
with families or other commitments.
Eye strain and other physical health issues
The industry can be affected by issues such as labor laws, trade agreements, and environmental
regulations, which can have an impact on job security and opportunities.
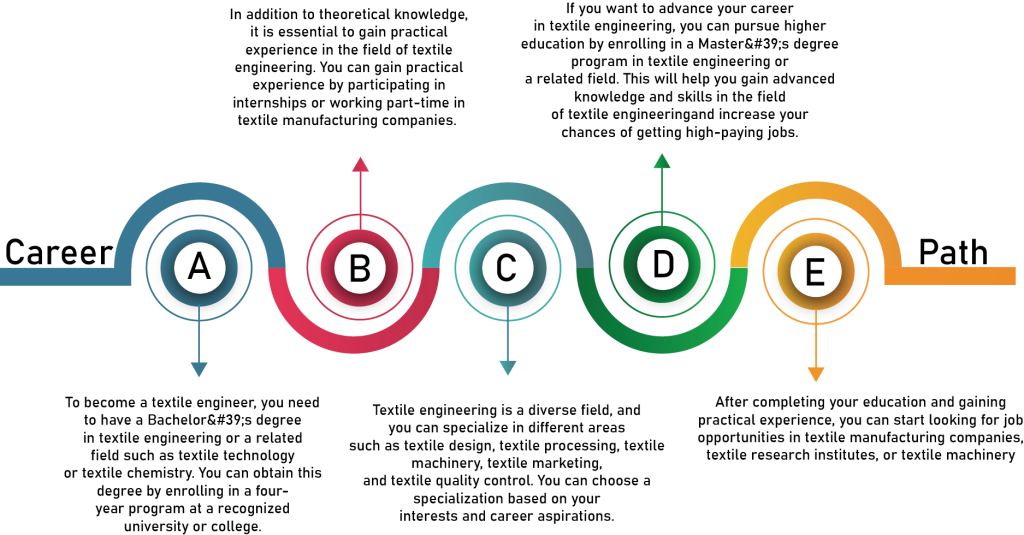
The cost of education to pursue a career in textile engineering in India can vary depending on several
factors, such as the type of institution, course duration, and location.
In India, there are several government and private institutions that offer undergraduate and
postgraduate programs in textile engineering. The fees for undergraduate programs can range from INR
50,000 to INR 3 lakhs per year, depending on the institution and program. For postgraduate programs,
the fees can range from INR 1 lakh to INR 5 lakhs per year. However, fees for some premium institutions
such as Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) or National Institute of Fashion Technology (NIFT) can be
higher.
Apart from tuition fees, there are other expenses that students may need to consider, such as
accommodation, transportation, textbooks, and other study materials. The cost of living can vary
depending on the location of the institution, with larger cities being more expensive than smaller towns.
[wpcharts type=”horizontalbarchart” bgcolor=”red:gray:yellow,blue:gray:yellow,random:gray:yellow,purple:gray:yellow” min=”0″ legend=”true” titles=”2 year , 5 year” values=”3,7,5,12″]
The earning potential of a textile engineer in India can vary depending on several factors such as
education, experience, location, and job role.
On average, a fresh graduate with a bachelor's degree in textile engineering can expect to earn a
starting salary of around INR 3-5 lakhs per annum. With experience, the salary can increase to INR 8-12
lakhs per annum. Textile engineers with a master's degree or a Ph.D. can earn higher salaries and can be
eligible for senior-level positions such as research and development, quality assurance, and production
management.
The earning potential can also vary based on the location of the job. Salaries in metro cities are typically
higher than those in smaller towns.
In addition to salaries, textile engineers in India can also earn bonuses and benefits such as health
insurance, retirement plans, and paid vacation time.
[wpcharts type=”horizontalbarchart” bgcolor=”red:gray:yellow,blue:gray:yellow,random:gray:yellow,purple:gray:yellow” min=”0″ legend=”false” titles=”Entry-Level, Mid-Career, Senior-Level ” values=”5,15,25,35,45,55″]
Strong foundation in mathematics and science.
Analytical and problem-solving skills.
Attention to detail.
Creativity and design skills.
Good communication and interpersonal skills.
Ability to work in a team.
Interest in textile products and their manufacturing processes.
Poor time management and procrastination.
Lack of attention to detail and quality control.
Inability to work in a team or collaborate with others.
Resistance to learning and adapting to new technologies and trends.
Lack of creativity and design skills.
Inadequate communication and interpersonal skills.
Limited knowledge and interest in mathematics and science.
Work-life balance
The work-life balance of a textile engineer can vary depending on their job responsibilities, work
environment, and personal preferences.
Textile engineers may work regular hours or have shifts that include weekends and evenings.
The workload and job responsibilities of a textile engineer can vary depending on their job position and
the company they work for.The workplace culture and management policies of a textile company can impact the work-life balance
of employees.
The personal priorities and responsibilities of a textile engineer outside of work can affect their ability to
maintain a work-life balance.
Overall, a textile engineer can achieve a work-life balance by prioritizing their work responsibilities and
delegating tasks when necessary and setting boundaries between work and personal life, such as
limiting after-hours work communication

It plays a vital role in the development of new fabrics and materials for various applications,
such as clothing, industrial textiles, medical textiles, and more.
As a textile engineer, you can work in various industries such as fashion, sports, automotive,
aerospace, and healthcare, among others.
Textile engineering offers numerous career opportunities, such as product development,
research and development, quality control, process engineering, and management.
Textile engineers can help reduce the environmental impact of textile production by developing
sustainable and eco-friendly materials and processes.
Textile engineering is a rapidly growing field with increasing demand for professionals who
possess the necessary skills and knowledge.
A career in textile engineering can be financially rewarding, with high earning potential and
opportunities for advancement.
Textile chemistry: It focuses on the chemical properties of fibers and fabrics, including dyeing, finishing,
and other chemical treatments.
Textile materials science: It focuses on the development of new materials for textile applications, such
as high-performance fibers and fabrics.
Fiber Science and Technology: Fiber science and technology is a specialization that focuses on the study
of fibers, including their chemical and physical properties, processing, and applications.
Textile Design and CAD: Textile design and CAD (computer-aided design) is a specialization that
combines creativity and technology to create textile products with unique designs and functionality.
CAD technology is also used to simulate textile products, allowing designers to test and refine their
designs before production.
Textile Manufacturing Processes: Textile manufacturing processes specialization involves the study of
the various processes involved in textile production, such as spinning, weaving, knitting, dyeing, printing,
and finishing.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, textile engineering offers a diverse range of specializations and career opportunities in
various industries. As a textile engineer, you can contribute to the development of new materials,
products, and technologies while also promoting sustainability and eco-friendliness in the industry. With
a high earning potential, job growth, and global impact, textile engineering is a rewarding and fulfilling
career choice for those with a passion for science, engineering, and creativity.