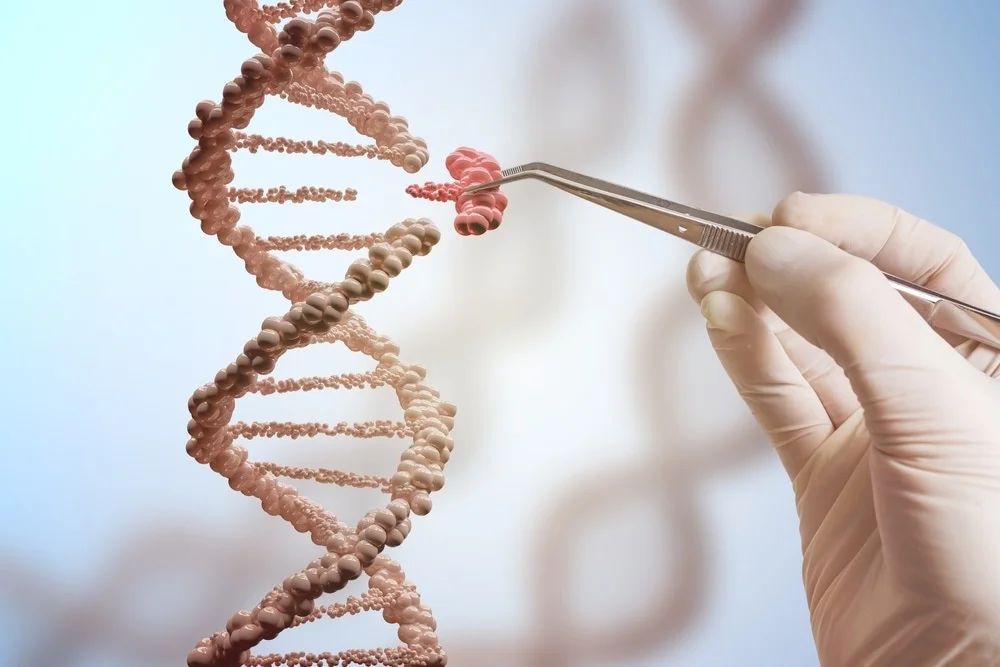
Medical genetics is a specialized branch of medicine that focuses on the diagnosis, management, and treatment of genetic disorders. It involves the study of genetic variation and its impact on human health, including the identification of genetic diseases, genetic counseling, and the development of new treatments.

Work description
Medical geneticists work with patients to diagnose and manage genetic conditions, provide genetic counseling to families, and design treatment plans that address the underlying genetic causes of disease. They may also conduct research into the genetic basis of diseases and develop new genetic tests and therapies.
High Demand
Opportunity to make a significant impact on patient care and outcomes.
Lucrative salaries
Ability to work with cutting-edge technology and stay up-to-date with rapidly evolving research.
Opportunities for innovation
Wide range of career paths, including clinical practice, research, teaching, and genetic counseling.
Versatility
High demand for medical geneticists due to the increasing prevalence of genetic diseases and personalized medicine.
Flexibility
Good earning potential, with handsome salaries.
High stress
Long and rigorous education and training, including medical school, residency, and fellowship programs.
Long hours
Limited job opportunities in some geographic regions and healthcare systems.
Competitive field
High emotional burden, as medical geneticists often work with patients and families affected by serious and life-limiting genetic conditions.
Constant learning
Ethical considerations, such as confidentiality, informed consent, and genetic discrimination, can be challenging to navigate.
Isolation
Rapidly changing regulatory landscape, with evolving laws and policies related to genetic testing and privacy.
Pursuing a career in medical genetics in India requires a significant investment of both time and money. The first step is to complete a Bachelor’s degree in a relevant field such as Biology or Genetics, which can take three to four years and cost anywhere from INR 50,000 to INR 3,00,000 per year depending on the college and location.
After obtaining a Bachelor’s degree, students may choose to pursue a Master’s degree in medical genetics, which can take two years and cost anywhere from INR 50,000 to INR 5,00,000 per year depending on the college and location.
To become a licensed medical geneticist, students will need to complete a residency program, which can take an additional three to four years and cost anywhere from INR 5,00,000 to INR 10,00,000 per year depending on the institution.
[wpcharts type=”horizontalbarchart” bgcolor=”red:gray:yellow,blue:gray:yellow,random:gray:yellow,purple:gray:yellow” min=”0″ legend=”true” titles=”2 year , 5 year” values=”3,7,5,12″]
In India, the average salary of a medical geneticist is around INR 10-12 lakhs per year. However, the average salary can vary depending on the location, organization, and level of experience.
[wpcharts type=”horizontalbarchart” bgcolor=”red:gray:yellow,blue:gray:yellow,random:gray:yellow,purple:gray:yellow” min=”0″ legend=”false” titles=”Entry-Level, Mid-Career, Senior-Level ” values=”5,15,25,35,45,55″]
Strong background in biology, genetics, and related sciences.
Critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
Excellent communication and interpersonal skills for working with patients and families.
Ability to work collaboratively as part of a multidisciplinary team.a
Compassion, empathy, and emotional intelligence to support patients and families affected by genetic conditions.
Attention to detail and strong organizational skills for managing patient records and test results.
Adaptability and willingness to learn as medical genetics is a rapidly evolving field.
Limited interest in biology or genetics as medical genetics requires a strong foundation in these subjects.
Poor communication skills, as medical geneticists work closely with patients and families.
Difficulty working collaboratively with other healthcare providers, as medical genetics often involves a multidisciplinary team approach.
Lack of empathy or emotional intelligence, as medical genetics deals with sensitive and potentially life-altering information for patients and families.
Inability to manage stress or cope with difficult situations, as medical genetics can involve challenging conversations and decision-making.
Inattention to detail, as accuracy and precision are critical in genetic testing and analysis.
Difficulty keeping up with rapidly evolving technology and research in the field.
Work-life balance
Clinical practice: Medical geneticists who work in clinical practice may have demanding schedules that involve seeing patients, interpreting test results, and collaborating with other healthcare providers. However, many medical genetics clinics prioritize work-life balance and may offer flexible schedules, part-time options, or remote work arrangements.
Research: Medical geneticists who work in research may have more control over their schedules and may have the ability to set their own hours. However, research positions may be highly competitive and require long hours, especially when working on grants or publications. Medical geneticists who work in industry may also have demanding schedules but may have more resources and support to manage workload and maintain work-life balance.
Genetic counseling: Genetic counselors may work in a variety of settings, including clinics, hospitals, and laboratories. Depending on the setting, they may have varying levels of control over their schedules. Genetic counselors who work in private practice or telehealth may have more flexibility to set their own hours and manage their workload.
Overall, medical genetics as a career can offer a good work-life balance, but this can depend on individual preferences, work environment, and job responsibilities. It’s important to consider these factors when pursuing a career in medical genetics and to prioritize self-care and work-life balance as part of a successful and fulfilling career.

Improved patient outcomes through early diagnosis and targeted treatment of genetic diseases.
Expanded knowledge of genetic diseases and their underlying mechanisms, leading to new treatments and potential cures.
Increased public awareness and understanding of genetic conditions, leading to decreased stigma and discrimination.
Advances in reproductive medicine, including preimplantation genetic diagnosis, prenatal testing, and genetic counseling.
Development of personalized medicine and precision therapies tailored to an individual’s genetic makeup.
Contribution to the broader field of medicine and healthcare, including collaborations with other specialists and multidisciplinary research teams.
Clinical Genetics
Clinical geneticists diagnose and treat genetic disorders through patient evaluation, family history analysis, and genetic testing.
Molecular Genetics
Molecular geneticists study the structure and function of genes and how changes in genes can lead to disease.
Cytogenetic
Cytogeneticists study the structure and function of chromosomes and how abnormalities in chromosome number or structure can cause genetic disorders.
Metabolic/Biochemical Genetics
Involves processing, analyzing, and interpreting large and complex data sets using statistical and computational methods.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, medical genetics is a promising career option, with a growing demand for trained professionals who can provide specialized care and expertise in the diagnosis and management of genetic disorders. With the right education, training, and experience, medical geneticists can have a rewarding career that makes a significant impact on human health and wellbeing.