Genetics is a fascinating field of study that has seen rapid growth in recent years. It is the study of genes, heredity, and genetic variation in living organisms. The field of genetics has numerous applications, including medical research, agriculture, forensics, and biotechnology. As a career choice, genetics offers many opportunities for growth and development. In this article, we will explore the work details, advantages, and disadvantages of genetics as a career in India.

Work description
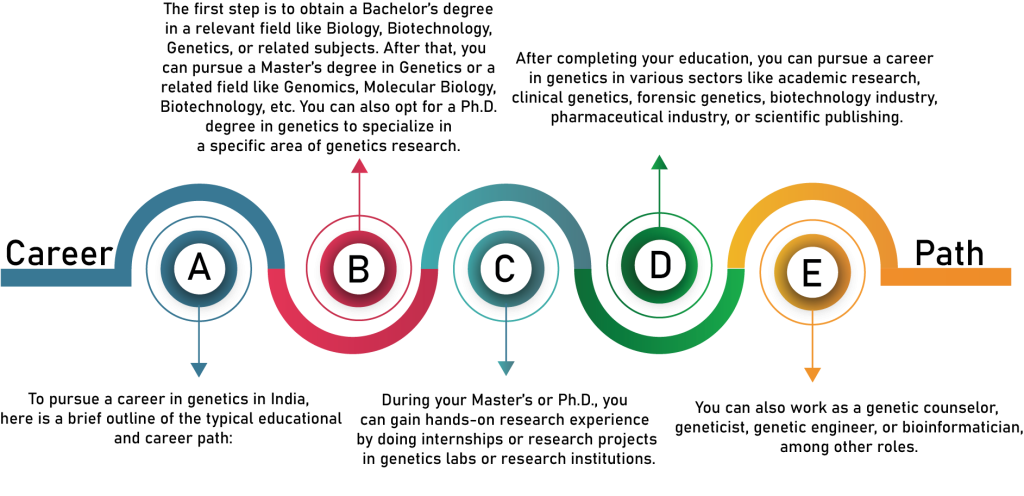
Genetics as a career in India involves the study of DNA and genes, their function, and their interaction with each other. Professionals in the field of genetics use a wide range of techniques and tools to analyze and manipulate genetic material. This includes DNA sequencing, PCR (polymerase chain reaction), gene editing tools like CRISPR, and genetic engineering.
Geneticists can work in various industries, including healthcare, agriculture, biotechnology, and research. They may also work in academia, teaching and conducting research in genetics. Some of the specific job roles in the field of genetics include genetic counselor, research scientist, bioinformatician, and genetic engineer.
High Demand
One of the primary advantages of a career in genetics is the potential for making a significant contribution to society.
Lucrative salaries
Genetic research has the potential to cure diseases, develop new medicines, and improve agricultural practices.
Opportunities for innovation
Genetic counselors can help individuals and families understand their risk of inherited conditions and make informed decisions about their health.
Versatility
Another advantage of a career in genetics is the diversity of job opportunities.
Flexibility
Geneticists can work in various industries, including healthcare, agriculture, biotechnology, and research.
Job satisfaction
The demand for geneticists is also expected to increase in the coming years as advancements in genetics and genomics continue.
High stress
One of the major disadvantages of genetics as a career is the rigorous academic and training requirements.
Long hours
A degree in genetics typically requires several years of education, including a bachelor’s degree in biology or genetics, followed by a master’s or doctoral degree. This can be time-consuming and financially draining.
Competitive field
With an increasing number of students interested in genetics, competition for jobs and research opportunities can be fierce.
Constant learning
Genetic research can be unpredictable and may require years of trial and error before any significant breakthroughs occur.
Isolation
There are ethical considerations to consider when working in genetics.
Eye strain and other physical health issues
Genetic research raises important questions about privacy, discrimination, and the appropriate use of genetic information.
The cost of pursuing a career in genetics in India can vary depending on several factors such as the type of degree program, the institution, and the duration of the program. Typically, undergraduate programs in genetics can cost between INR 20,000 to 1,00,000 per year while postgraduate programs can cost anywhere from INR 50,000 to 2,00,000 per year.
Additionally, pursuing a research-based career in genetics may require further investment in terms of equipment and resources, which can range from a few thousand rupees to several lakhs of rupees depending on the scope of the research. Overall, the cost of pursuing a career in genetics in India can range from a few lakhs to a few crores depending on the level of education and career path chosen.
[wpcharts type=”horizontalbarchart” bgcolor=”red:gray:yellow,blue:gray:yellow,random:gray:yellow,purple:gray:yellow” min=”0″ legend=”true” titles=”2 year , 5 year” values=”3,7,5,12″]
The earning potential of someone with a career in genetics in India can vary widely depending on several factors such as their level of education, work experience, and specific job role.
In general, entry-level positions such as research assistants and laboratory technicians may earn a salary of around INR 2-4 lakhs per annum, while more senior positions such as research scientists and professors may earn a salary of INR 10-20 lakhs per annum or higher.
The salary range can also vary depending on the industry, with the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries generally offering higher salaries than academic or government research positions.
Additionally, pursuing advanced degrees such as a Ph.D. in genetics can open up higher-paying job opportunities in academia, research, and industry. Overall, the earning potential for a career in genetics in India can range from moderate to high depending on the specific career path and level of education and experience.
[wpcharts type=”horizontalbarchart” bgcolor=”red:gray:yellow,blue:gray:yellow,random:gray:yellow,purple:gray:yellow” min=”0″ legend=”false” titles=”Entry-Level, Mid-Career, Senior-Level ” values=”5,15,25,35,45,55″]
Strong foundation in biology and chemistry.
Analytical and critical thinking skills.
Interest and passion for scientific research and discovery.
Attention to detail and ability to perform meticulous laboratory work.
Ability to work well in a team and collaborate with others.
Good communication skills to present research findings and collaborate with colleagues.
Familiarity with computer programs and data analysis software.
Poor attention to detail and difficulty with meticulous laboratory work.
Lack of interest in scientific research and discovery.
Limited analytical and critical thinking skills.
Poor communication skills and difficulty presenting research findings and collaborating with colleagues.
Dislike or lack of familiarity with computer programs and data analysis software.
Limited problem-solving skills and difficulty with complex genetic problems and challenges.
Impatience or lack of persistence to conduct experiments and complete long-term research projects.
Work-life balance
The work-life balance of someone in a genetics career can vary depending on their specific job and responsibilities. However, here are some general insights:
For those who work in research-oriented roles, the work-life balance may depend on the stage of research they are in. During intense research phases, work hours may be longer and may require working on weekends or holidays to meet project deadlines. However, during less busy periods, they may have a more flexible schedule and work from home.
In clinical roles such as genetic counselors or clinical geneticists, work hours may be more structured and predictable. Typically, these roles involve working with patients and their families, which may require some flexibility with schedules. However, these roles may offer more stable hours overall and may allow for a better work-life balance.
In biotechnology or pharmaceutical industry roles, work-life balance may depend on the company culture and specific role. Some companies may have more flexible hours and offer opportunities for remote work, while others may require more in-person work or have more rigid schedules.

Genetics professionals play a crucial role in advancing medical research and developing treatments for genetic disorders and diseases.
Geneticists can identify disease risk factors and develop targeted public health interventions.
Genetics careers require ethical considerations, as genetic testing and counseling can have significant personal and societal impacts.
Genetics careers are helping to usher in the era of personalized medicine.
Genetics professionals are in high demand in biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries.
Genetics careers offer numerous opportunities for career growth and specialization, as the field continues to expand and evolve rapidly.
Molecular Genetics
The study of the structure and function of genes at a molecular level, including DNA, RNA, and proteins.
Genomics security
The study of the entire genome of an organism, including its structure, function, evolution, and variation.
Population Genetics
The study of genetic variation within and between populations, and how it evolves ver time.
Developmental Genetics
The study of the genetic mechanisms that control the development and differentiation of cells and organisms.
Evolutionary Genetics
The study of the genetic mechanisms and processes that drive evolution, including natural selection, genetic drift, and mutation.
Conclusion:
Genetics is a rapidly evolving field with numerous opportunities for growth and development. As a career choice, it offers the potential for making a significant contribution to society, a diverse range of job opportunities, and financial rewards. However, the rigorous academic and training requirements, highly competitive nature of the field, and ethical considerations should be taken into account before embarking on a career in genetics. Ultimately, those who are passionate about genetics and committed to making a positive impact on society can find a fulfilling career in this exciting field.