Neuroscience is a rapidly growing field of study that involves the scientific study of the nervous system and its relationship to behavior, cognition, and other brain functions. It encompasses a range of disciplines, including biology, psychology, physics, and engineering, to investigate how the brain works, how it processes information, and how it produces behavior. Researchers in neuroscience study the nervous system at different levels of complexity, from individual neurons to large-scale brain networks.
Work description
Neuroscience is a broad field that encompasses various sub-disciplines, including neuroanatomy, neurophysiology, neuropsychology, and neuroimaging. Professionals in this field conduct research and studies on the structure, function, and disorders of the brain and nervous system. Some of the job responsibilities of a neuroscience professional include:
- Conducting experiments and studies to gain a better understanding of the brain and its functions
- Analyzing data and interpreting research results
- Developing new treatment methods for neurological disorders
- Diagnosing and treating patients with neurological disorders
- Conducting clinical trials for new drugs and treatments
- Teaching and mentoring students in the field of neuroscience
Exciting and fulfilling career
Neuroscience offers a challenging and dynamic career path that allows individuals to make a significant contribution to society by advancing our understanding of the brain and nervous system.
High demand
With an increasing incidence of neurological disorders such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease, there is a high demand for skilled professionals in this field.
Growth potential
The field of neuroscience is rapidly expanding with new developments and discoveries, providing ample opportunities for career growth and advancement.
Competitive salary
Professionals in this field are highly valued, and their services are well-compensated, with many opportunities for career growth and advancement.
Extensive education and training
Becoming a neuroscience professional requires a significant investment of time and resources. Individuals must complete a degree in neuroscience or a related field, followed by several years of training and practical experience.
Long working hour
Neuroscience professionals often work long hours, including weekends and holidays, to meet research and clinical demands.
Emotional strain
Diagnosing and treating patients with neurological disorders can be emotionally challenging and stressful, requiring a high level of compassion and resilience.
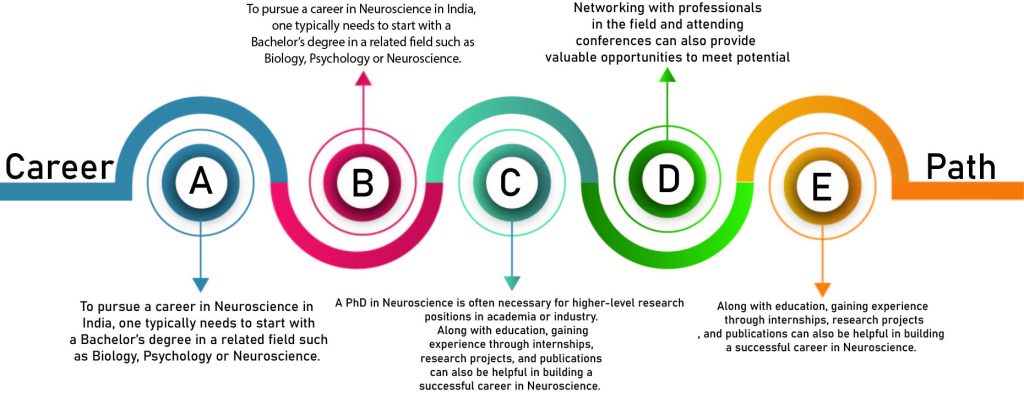
The cost of pursuing a career in Neuroscience in India varies depending on the level of education and the institution of choice.
Pursuing a Bachelor’s degree in Neuroscience can cost anywhere from INR 50,000 to INR 2,00,000 per year, while a Master’s degree can cost INR 1,00,000 to INR 4,00,000 per year. PhD programs in Neuroscience are usually fully-funded, so there are no tuition fees involved.
However, students will still need to cover their living expenses, which can range from INR 10,000 to INR 50,000 per month depending on the city they are living in. Additionally, there may be additional costs such as lab fees, equipment expenses, and research costs.
[wpcharts type=”horizontalbarchart” bgcolor=”red:gray:yellow,blue:gray:yellow,random:gray:yellow,purple:gray:yellow” min=”0″ legend=”true” titles=”2 year , 5 year” values=”3,7,5,12″]
The earning potential of someone with a career in Neuroscience in India can vary depending on their level of education and experience.
As a general rule, those with higher levels of education and experience in the field can expect to earn higher salaries. Entry-level positions such as research assistants or lab technicians can earn around INR 2,50,000 to INR 4,00,000 per year.
With a Master’s degree or PhD, one can expect to earn higher salaries in academic or research positions, ranging from INR 6,00,000 to INR 15,00,000 per year.
Those with a strong background in the field can also earn a higher salary in the private sector or in pharmaceutical companies.
[wpcharts type=”horizontalbarchart” bgcolor=”red:gray:yellow,blue:gray:yellow,random:gray:yellow,purple:gray:yellow” min=”0″ legend=”false” titles=”Entry-Level, Mid-Career, Senior-Level ” values=”5,15,25,35,45,55″]
Strong foundation in biology, chemistry, and mathematics
Analytical thinking and problem-solving skills
Attention to detail and precision
Ability to work independently and in a team
Good communication skills, both written and verbal
Curiosity and a passion for exploring the complexities of the brain and behavior
Persistence and patience in conducting experiments and analyzing data
Lack of interest or curiosity in the workings of the brain and behavior
Difficulty in grasping complex scientific concepts and theories
Poor time management skills and difficulty meeting deadlines
Difficulty working with others in a collaborative environment
Limited ability to handle stressful situations, such as research setbacks or failures
Inadequate ethical standards and lack of responsibility in conducting research
Inability to handle the physical and emotional demands of laboratory work, such as long hours of standing or exposure to potentially hazardous materials.
Work-life balance
The work-life balance of a neuroscientist can vary depending on the individual’s research area, work environment, and personal preferences. However, here are some general aspects of the work-life balance that a neuroscientist may experience:
Workload: Neuroscientists often work long hours, including weekends and evenings, to meet research deadlines and conduct experiments. However, some neuroscientists may have more flexible schedules, such as those who teach or work in industry.
Research environment: Depending on the type of research being conducted, a neuroscientist may work in a laboratory, office, or field setting. Some research areas, such as clinical neuroscience, may involve working with patients.
Work location: The location of work can also affect the work-life balance, as some environments may be more conducive to flexible schedules or remote work.
Personal life: Maintaining a healthy work-life balance can involve prioritizing self-care, spending time with family and friends, pursuing hobbies and interests, and taking breaks from work when needed.

Understanding of brain function and disorders
Development of therapies and treatments for neurological conditions
Advancements in technologies for brain imaging and manipulation
Integration of neuroscience with other fields such as psychology, computer science, and engineering
Contribution to education and public awareness about brain health and neuroscience research
understanding various neurological and psychiatric disorders.
Behavioral Neuroscience
Examines the relationship between behavior and the brain, including how the nervous system mediates behavior and how behavior affects the brain.
Cognitive Neuroscience
Studies the neural basis of cognitive processes, including perception, attention, memory, language, and decision making.
Clinical Neuroscience
Focuses on the diagnosis and treatment of neurological and psychiatric disorders, including stroke, Alzheimer’s disease, depression, and anxiety.
Computational Neuroscience
Develops mathematical and computational models to simulate neural systems and understand their function.
Developmental Neuroscience
Investigates how the brain develops from prenatal stages through adulthood, including the role of genetics and environmental factors.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, neuroscience is an exciting and rewarding career option, with ample opportunities for growth and advancement. While it may require a significant investment of time and resources, the rewards of this field make it a worthwhile pursuit for those interested in science and healthcare