Microbiology is a branch of science that deals with the study of microscopic organisms such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and algae. A microbiologist is a scientist who specializes in the study of these microorganisms, including their structure, genetics, metabolism, and ecological roles. In this article, we will discuss the work description, advantages and disadvantages, earning potential, career path, strengths, and weaknesses required to become a microbiologist, work-life balance, impacts of the career, and possible specializations.
Work description
A microbiologist’s primary job is to conduct research to identify and study microorganisms, including their properties, characteristics, and interactions with other organisms. They may also work in industries such as food, pharmaceuticals, or healthcare to ensure products are safe for human use. Some typical job duties of a microbiologist may include:
- Collecting and analyzing samples of microorganisms from various sources.
- Conducting experiments and tests to determine the behavior of microorganisms under different conditions.
- Isolating and identifying different kinds of microorganisms.
- Developing and testing new drugs or treatments to combat infectious diseases.
- Developing and implementing strategies for preventing the spread of infectious diseases.
- Writing scientific reports, research papers, or grant proposals.
High Demand
Exciting and meaningful work that contributes to public health and safety.
Lucrative salaries
Opportunities for advancement and career growth.
Opportunities for innovation
High demand for skilled microbiologists in various industries.
Versatility
Opportunities to work in diverse settings, including academia, government, and private industry.
Flexibility
Flexibility to work in different research areas and specializations.
High stress
Long hours in the lab for work and research.
Long hours
Potential exposure to hazardous microorganisms or chemicals.
Competitive field
Intense competition for funding and research positions.
Constant learning
High-pressure environment to publish research results.
Isolation
Limited job opportunities in certain areas.
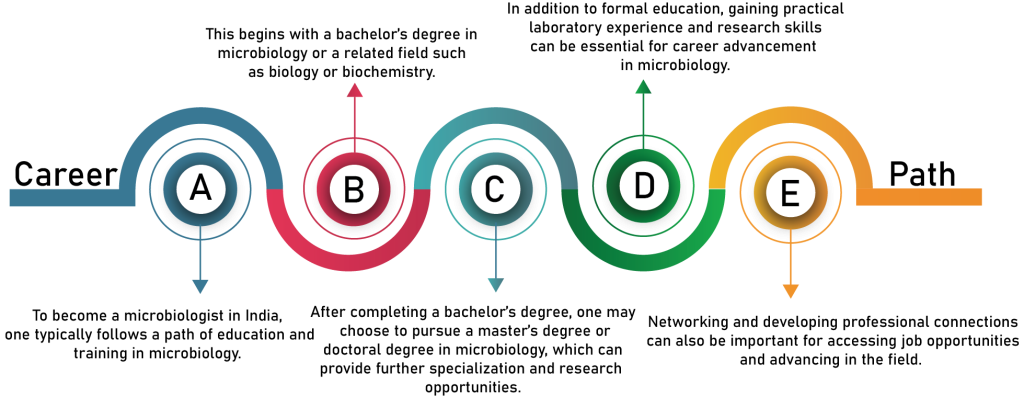
The cost of becoming a microbiologist in India can vary depending on the level of education and the institution attended. Pursuing a bachelor’s degree in microbiology at a government-funded university can cost anywhere from INR 10,000 to INR 50,000 per year, while a private institution may charge INR 50,000 to INR 1,00,000 per year.
Pursuing a master’s degree in microbiology may cost INR 50,000 to INR 1,00,000 per year, and a doctoral degree may cost INR 1,00,000 to INR 2,00,000 per year.
Additional costs may include expenses for textbooks, laboratory materials, and research projects. Overall, the cost of becoming a microbiologist in India can be relatively affordable compared to other countries, but it is important to research and compare costs of different institutions before making a decision.
[wpcharts type=”horizontalbarchart” bgcolor=”red:gray:yellow,blue:gray:yellow,random:gray:yellow,purple:gray:yellow” min=”0″ legend=”true” titles=”2 year , 5 year” values=”3,7,5,12″]
The earning potential of a microbiologist in India can vary depending on the level of education, experience, and industry. According to payscale.com, the average salary for a microbiologist in India is around INR 360,000 per year. Entry-level microbiologists with a bachelor’s degree may earn around INR 200,000 to INR 400,000 per year, while those with a master’s degree may earn around INR 400,000 to INR 800,000 per year. Experienced microbiologists in industries such as pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and healthcare may earn higher salaries, ranging from INR 800,000 to INR 1,500,000 per year or more.
[wpcharts type=”horizontalbarchart” bgcolor=”red:gray:yellow,blue:gray:yellow,random:gray:yellow,purple:gray:yellow” min=”0″ legend=”false” titles=”Entry-Level, Mid-Career, Senior-Level ” values=”5,15,25,35,45,55″]
Strong analytical and problem-solving skills.
Attention to detail.
Ability to work independently and collaboratively.
Good communication and interpersonal skills.
Proficient in scientific methods and laboratory techniques.
Lack of attention to detail or poor organizational skills.
Inability to adapt to changing technologies and trends.
Lack of interest or passion for the field.
Poor communication or teamwork skills.
Inadequate math and science skills.
Impatience or inability to work through complex problems.
Tendency to procrastinate or miss deadlines.
Work-life balance
The work-life balance of a microbiologist can vary depending on the specific job and industry. In research positions, long hours of lab work and research are common, which may affect work-life balance. However, some microbiologists work in government or private industry, where standard working hours are typical. Microbiologists may also have the opportunity to attend scientific conferences or travel for research purposes, which may impact work-life balance.

Microbiology is a crucial field that impacts public health and safety.
Microbiologists play a vital role in developing new drugs, vaccines, and treatments for infectious diseases.
They also work to prevent the spread of infectious diseases through public health measures, such as vaccination programs and food safety regulations.
Microbiologists play a critical role in environmental conservation and research, studying microorganisms’ impact on ecosystems and identifying ways to protect them.
Medical microbiology
studying microorganisms that cause human diseases and developing treatments and vaccines.
Environmental security
studying microorganisms in the environment, including soil, water, and air, and their impact on ecosystems.
Industrial microbiology
using microorganisms to produce products such as food, drugs, and chemicals.
Food microbiology
ensuring the safety and quality of food products by studying microorganisms that grow in food and developing measures to prevent foodborne illnesses.
Veterinary microbiology
studying microorganisms that affect animals, including livestock and pets, and developing treatments and vaccines.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, a career as a microbiologist can be exciting and meaningful, with opportunities for growth and advancement in various industries. However, it also requires dedication and hard work, with long hours of lab work and research. Students interested in pursuing a career in microbiology should have strong analytical and problem-solving skills, attention to detail, and proficiency in scientific methods and laboratory techniques. They should also be prepared for intense competition for funding and research positions and potential exposure to hazardous microorganisms or chemicals. Overall, microbiology is a critical field that impacts public health and safety, environmental conservation, and scientific advancement.