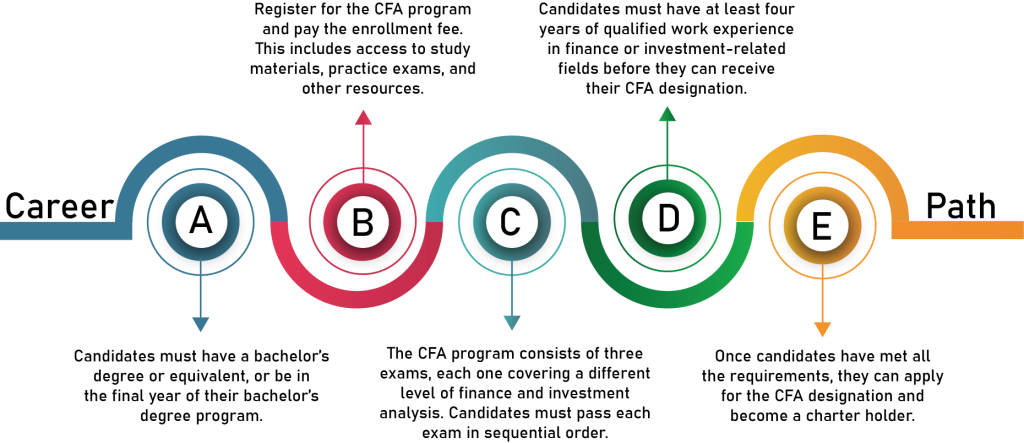
Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA) is a professional designation granted by the CFA Institute to financial and investment professionals who have completed a rigorous program of study, passed a series of three exams, and accumulated relevant work experience. The program covers a broad range of topics related to finance, including investment analysis, portfolio management, economics, and ethics. CFA charter holders are considered experts in financial analysis and often work in fields such as investment banking, asset management, and financial research. The designation is highly respected in the finance industry and is recognized worldwide.

Work description
The work description of a Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA) typically involves conducting in-depth financial analysis to support investment decisions, managing investment portfolios, and providing financial advice to clients.
They use their knowledge and skills in financial analysis, portfolio management, risk management, and financial reporting to evaluate investment opportunities and make recommendations to clients.
They also conduct research and analysis of economic and financial data to stay abreast of market trends and conditions. CFAs may work for investment banks, asset management firms, hedge funds, or other financial institutions. They may also work as independent consultants, providing financial advice to individual clients.
The work of a CFA requires a high level of analytical and quantitative skills, attention to detail, and strong communication and interpersonal skills.
Widely recognized and respected credential in the finance industry.
Demonstrates a high level of expertise and commitment to the profession.
Provides a broad and comprehensive knowledge of finance, economics, and investment analysis.
Versatility
Enhances career prospects and earning potential.
Flexibility
Opportunities for networking and professional development
Rigorous program requires significant time and effort to complete.
High costs associated with exam fees, study materials, and ongoing continuing education requirements.
Limited specialization in a specific area of finance.
Constant learning
May not guarantee job opportunities or career advancement.
Isolation
Credential may become less relevant or obsolete over time due to changes in the industry or technology.
The cost of pursuing a career in Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA) in India can vary depending on several factors, such as the cost of study materials, exam fees, and membership dues. Here are some estimated costs:
CFA Program Enrollment fees: INR 33,000 (for all three levels combined).
CFA Exam registration fees: The cost of registration for each exam level increases the closer you get to the exam date. The registration fees for each level of the CFA exam in India are approximately:
Level 1: INR 51,000 – 74,000
Level 2: INR 74,000 – 89,000
Level 3: INR 74,000 – 89,000
CFA Exam Preparation Materials: The cost of study materials for the CFA program can vary depending on the provider you choose. The total cost of study materials can range from INR 22,000 to 73,000.
Overall, the approximate cost of completing the CFA program in India can range from INR 1,80,000 to 4,50,000, depending on the above factors.
The earning potential of a Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA) in India can vary widely depending on factors such as years of experience, industry, job role, and location. Here are some estimated salary ranges for CFAs in India:
Entry-level CFA: ₹6-8 lakhs per annum
Mid-career CFA: ₹12-20 lakhs per annum
Senior-level CFA: ₹30-50 lakhs per annum or more
It’s important to note that earning potential can also be influenced by factors such as job performance, industry trends, and the overall economic climate.
Strong analytical and quantitative skills.
Detail-oriented and highly organized.
Ability to work independently and in teams.
Excellent communication and interpersonal skills.
Interest and passion for finance and investment analysis.
Willingness to continuously learn and adapt to changes in the industry.
Poor time management skills.
Lack of discipline and focus.
Lack of interest or passion for the field.
Poor communication or teamwork skills.
Inadequate math and science skills.
Inability to communicate effectively with clients and colleagues.
Lack of interest in finance and investment analysis.
Work-life balance
As a Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA), work-life balance can vary depending on the specific job and industry. However, in general, CFAs tend to work long hours and may have a demanding workload, particularly during busy periods such as the end of the quarter or fiscal year.
Many CFAs work in investment banking or asset management, where they may need to be available to clients or monitor market fluctuations outside of regular business hours. This can lead to a need for flexibility in their work schedule, which may impact their personal life.
However, some CFAs work for corporations, government agencies, or non-profit organizations, which may offer more predictable hours and a better work-life balance. CFAs may also have the opportunity to work remotely, which can allow for greater flexibility in balancing work and personal life.

Potential for high earning potential and job security.
Opportunity to work in a dynamic and constantly evolving industry.
Development of valuable skills in finance and investment analysis.
Opportunity to work in a global environment and network with other finance professionals worldwide.
Ability to make a positive impact on clients’ financial goals and objectives.
High level of competition in the industry, which can lead to stress and burnout.
Credit Analyst
Evaluates the creditworthiness of individuals or companies applying for loans, to determine the level of risk involved in lending money.
Research Analyst
Analyzes financial data and industry trends to provide investment recommendations to clients or fund managers.
Portfolio Management
Focuses on constructing and managing investment portfolios on behalf of clients or institutions
Financial Planning and Analysis Machine Learning
Involves developing financial plans and forecasting future financial performance for a company or organization.
Investment Management
Focuses on managing investment portfolios to achieve clients’ financial goals and objectives.