A certified financial planner (CFP) is a professional who has achieved a recognized standard of competence in the field of financial planning. The certification is granted by the Certified Financial Planner Board of Standards, Inc. (CFP Board), a non-profit organization based in the United States.
A CFP is a financial professional who can help individuals and families manage their finances by creating a comprehensive financial plan that includes retirement planning, investment management, tax planning, estate planning, and risk management. The CFP must act in the best interests of their clients and adhere to a strict code of ethics.

Work description
The work description of a certified financial planner typically includes:
Meeting with clients to understand their financial goals, objectives, and risk tolerance.
Analyzing clients’ financial information, including income, expenses, assets, and liabilities.
Developing a comprehensive financial plan that includes investment strategies, retirement planning, tax planning, estate planning, and risk management.
Providing advice on financial matters, including investment choices, insurance coverage, and debt management.
Monitoring clients’ progress toward their financial goals and making adjustments to their financial plan as necessary.
Maintaining up-to-date knowledge of financial products, tax laws, and investment trends.
High earning
High earning potential.
Lucrative salaries
Opportunities for career advancement.
Opportunities for innovation
Flexibility in work schedule and work location.
Versatility
Opportunity to help people achieve their financial goals.
Flexibility
Variety in work tasks and client base.
Job satisfaction
Increasing demand for financial planning services.
High stress
Intense competition for clients and jobs.
Requires significant education, training, and certification
Competitive field
Requires strong communication and interpersonal skills.
Can be a stressful job with high levels of responsibility and liability.
Isolation
May require long hours, especially during tax season or when working with clients in different time zones.
Eye strain and other physical health issues
Can be affected by market fluctuations and economic conditions.
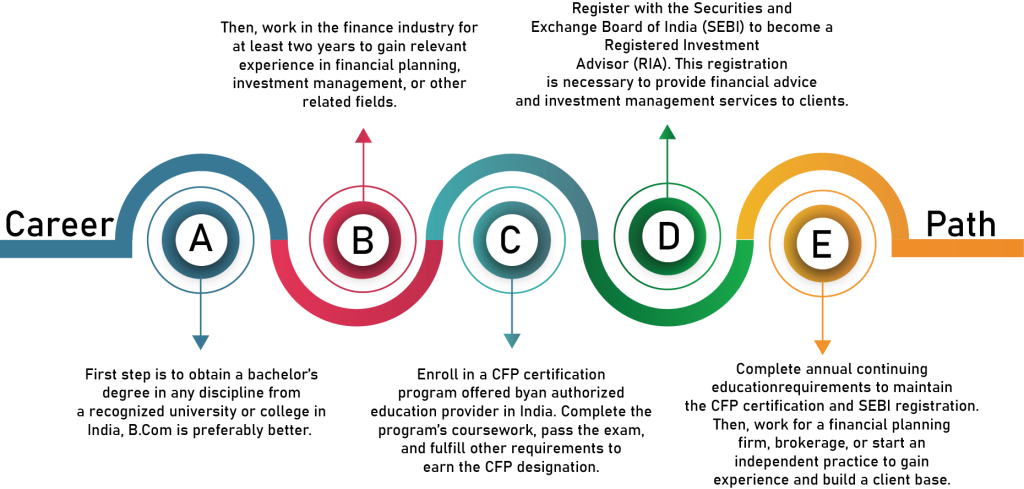
The cost of pursuing a career in certified financial planning in India can vary depending on various factors such as the mode of education, the institution, the duration of the program, and the location. However, here are some approximate costs associated with becoming a certified financial planner in India:
Education and Training:
A bachelor’s degree in any discipline: ₹50,000 – ₹2,00,000
Certified Financial Planner (CFP) certification program: ₹75,000 – ₹2,50,000
Exam Fees:
CFP Exam registration fee: ₹20,000 – ₹25,000
CFP Exam fees per module: ₹7,500 – ₹12,000
Additional expenses like living expenses, transportation, books and study materials can add up to this cost. Also, these costs are estimated and can vary widely based on individual preferences and circumstances.
[wpcharts type=”horizontalbarchart” bgcolor=”red:gray:yellow,blue:gray:yellow,random:gray:yellow,purple:gray:yellow” min=”0″ legend=”true” titles=”2 year , 5 year” values=”3,7,5,12″]
The earning potential of a certified financial planner in India depends on several factors such as the years of experience, education, certification, location, and the type of firm or organization they work for.
Entry-level CFPs can earn ₹3,00,000 – ₹5,00,000 per annum, and experienced CFPs can earn ₹6,00,000 – ₹15,00,000 per annum. CFPs with 10+ years of experience can earn upwards of ₹20,00,000 per annum.
CFPs can earn commissions ranging from 0.5% to 2% of the client’s assets under management (AUM). The commission can vary based on the size of the client’s portfolio, the type of financial product, and the firm’s compensation structure.
Many financial planning firms offer bonuses based on performance, client acquisition, or revenue targets. The bonus can range from a few thousand rupees to several lakhs per annum.
[wpcharts type=”horizontalbarchart” bgcolor=”red:gray:yellow,blue:gray:yellow,random:gray:yellow,purple:gray:yellow” min=”0″ legend=”false” titles=”Entry-Level, Mid-Career, Senior-Level ” values=”5,15,25,35,45,55″]
Strong problem-solving skills.
Analytical thinking and attention to detail.
Strong work ethic and attention to detail.
Interest in financial markets and investment management.
Good communication and teamwork skills
Inability to work under pressure and meet deadlines.
Resistance to change or adapt to new technologies or regulations.
Lack of interest in finance and investment management.
Poor communication or teamwork skills.
Inadequate math and science skills.
Impatience or inability to work through complex problems.
Lack of interest in finance and investment management.
Work-life balance
The work-life balance of a certified financial planner can vary depending on their work environment, clients, and business model.
CFPs typically work 40-50 hours per week, but this can vary depending on the workload, client needs, and market conditions. Some CFPs work regular office hours, while others may need to work evenings or weekends to accommodate client schedules.
CFPs work with clients who have varying needs, investment objectives, and risk tolerance levels. They may need to spend extra time understanding their clients’ financial situation, goals, and preferences to provide tailored advice and solutions.
CFPs can work for financial planning firms, brokerages, or start their own independent practices. The work-life balance can vary based on the business model, with independent CFPs having more control over their schedules and workload.

CFPs help clients create and implement financial plans to achieve their long-term financial goals and increase their financial stability.
CFPs provide investment management services to help clients maximize their returns and manage their investment risks.
CFPs assist clients in creating retirement plans, including setting retirement goals, estimating expenses, and determining the savings required to achieve these goals.
CFPs help clients assess and manage financial risks, such as market risks, inflation risks, and life events risks.
CFPs assist clients in tax planning, including identifying tax-saving opportunities and optimizing tax efficiency.
CFPs help clients with estate planning, including creating wills and trusts, and minimizing estate taxes.
Retirement Planning Machine Learning
Specializes in creating retirement plans, including setting retirement goals, estimating expenses, and determining the savings required to achieve these goals.
Tax Planning
Specializes in identifying tax-saving opportunities and optimizing tax efficiency for clients.
Estate Planning
Specializes in creating wills and trusts, and minimizing estate taxes.
Insurance Planning Machine Learning
Focuses on identifying insurance needs and developing strategies to manage financial risks, such as health, disability, and long-term care insurance.
Education Planning
Specializes in planning for education expenses, such as college or university fees, and identifying sources of funding.